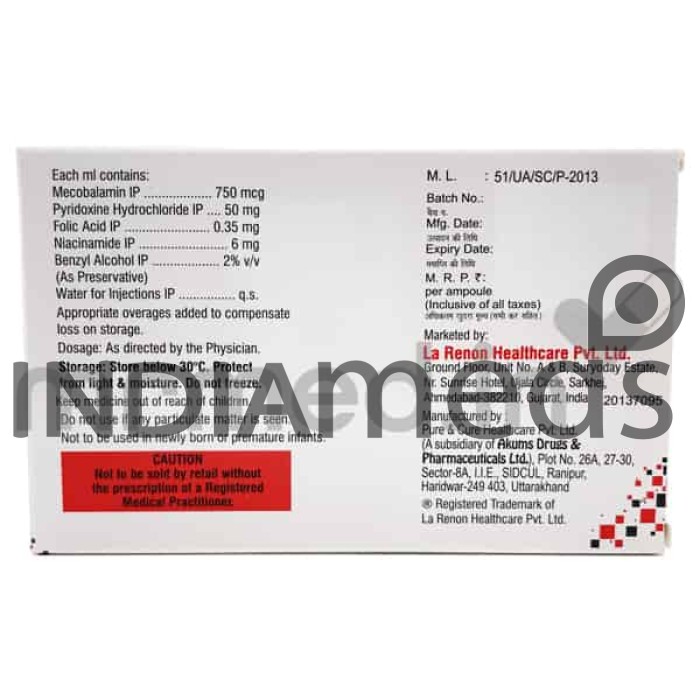
Eido Injection contains a combination of Mecobalamin (a form of Vitamin B12), Pyridoxine hydrochloride (Vitamin B6), Folic acid (Vitamin B9), and Niacinamide (a form of Vitamin B3). It belongs to the medication class known as a vitamin supplement. This medication is used to treat patients suffering from essential water-soluble vitamin deficiency after hemodialysis, particularly in patients with end-stage renal disease who have increased requirements for these vitamins.
Mecobalamin controls various bodily processes like cell growth, blood formation, and protein synthesis. Pyridoxine HCl is involved in metabolizing proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Folic acid is essential for red blood cell formation, multiplication, and maturation. Niacinamide helps in energy production and enzyme function. Do not consume Eido Injection if you are allergic to Mecobalamin, Pyridoxine Hcl, Niacinamide, or any of its ingredients in the medication.
Before taking Eido Injection, inform your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to get pregnant, or think you may be pregnant or if you are breastfeeding. Before starting the treatment, inform your doctor if you have a history of liver or kidney disorders. This medicine should be given to children only when the doctor has prescribed it.
Therapeutic Effects of Eido Injection
Pregnancy
It is unknown whether Eido Injection is harmful to the unborn baby. Notify your healthcare professional if you are pregnant or planning to have a baby think you may be pregnant.
Breast Feeding
It is unknown whether Eido Injection is excreted in breast milk. So, before starting the treatment, inform your doctor if you are breastfeeding. Contact your doctor for more information.
Lungs
It is unknown whether Eido Injection is safe for patients with lung problems. Inform your physician if you have any lung disease before starting the treatment. Contact your doctor if you experience any lung-related symptoms.
Liver
It is unknown whether Eido Injection is safe for patients with liver problems. Inform your physician if you have any liver disease before starting the treatment. Contact your doctor if you experience any liver-related symptoms.
Alcohol
It is unknown whether consuming alcohol while taking Eido Injection is safe. Please speak with your physician.
Driving
It is unknown whether Eido Injection alters driving ability. However, if you experience side effects like tiredness or drowsiness, avoid driving and using machines.
Common
- Headache
- Itching
- Swelling
- Nervousness
- Anxiousness
- Loss of hunger
- Dizziness
- Upset stomach
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Pain at the injection site
To manage the side effects of Eido Injection, follow the prescribed dosage, and report side effects promptly. Stay hydrated, and monitor blood sugar levels. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by following a balanced diet and attending follow-up appointments.
Yes, Eido Injection can interact with other medications and can cause undesirable side effects. Inform your doctor about any prescribed medications, over-the-counter medicines, nutritional or vitamin supplements, and herbal products you take or have taken before the treatment.
Common side effects of Eido Injection include headache, itching, swelling, nervousness, anxiousness, and loss of hunger. Dizziness, upset stomach, diarrhea, constipation, pain at the injection site. It is crucial to consult your doctor for any concerns or persistent side effects.
Information regarding using Eido Injection during pregnancy and breastfeeding is unknown. So, getting healthcare professionals' advice before consuming the medicine is recommended. The potential benefits and risks of the medicine should be carefully assessed.
Patients with kidney disorders should consume Eido Injection cautiously. Before starting the treatment,t inform your doctor about all the underlying conditions.
| Molecule Name: Mecobalamin + Pyridoxine hydrochloride + Folic acid + Niacinamide | Therapeutic class: Supplement |
| Pharmacological class: Vitamin supplement | Indications: 1. Treatment of vitamin deficiency after hemodialysis 2. Hyperhomocysteinemia in End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) |